In an era marked by globalization, evolving customer demands, and intense competition, businesses are increasingly looking for ways to streamline their operations. Lean supply chain management has emerged as a powerful approach to achieving efficiency, reducing waste, and delivering maximum value to customers. By applying the principles of Lean, companies can transform their supply chains into highly efficient and responsive systems, gaining a significant competitive edge.
What is Lean Supply Chain Management?
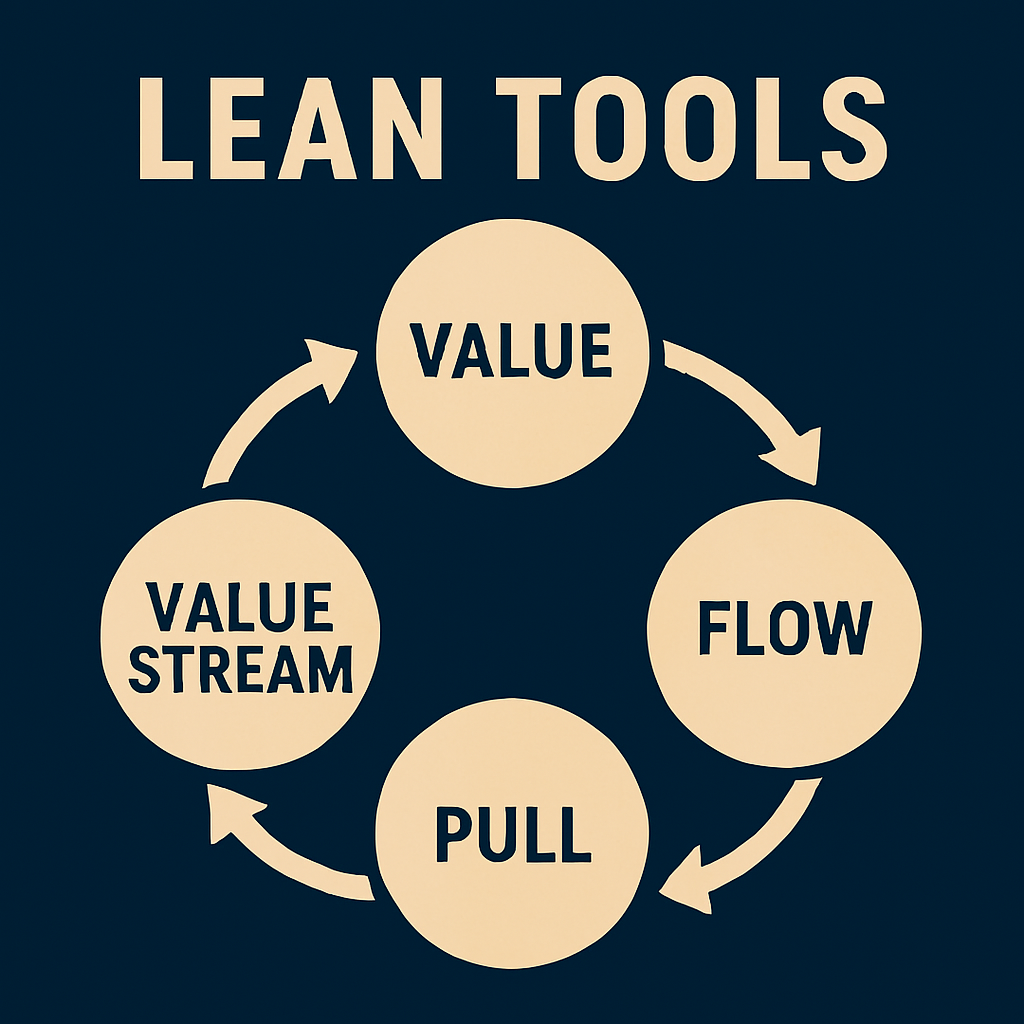
Lean supply chain management focuses on minimizing waste while maximizing value across the entire supply chain. The concept is rooted in the Lean manufacturing philosophy pioneered by Toyota, which emphasizes the elimination of activities that do not add value to the end customer. In the context of supply chain management, this includes reducing excess inventory, minimizing transportation costs, and optimizing production processes.
Key Principles of Lean in Supply Chain Management
- Eliminate Waste: Waste can take many forms, including overproduction, excess inventory, unnecessary transportation, and inefficient processes. Identifying and eliminating these sources of waste is at the core of Lean principles.
- Continuous Improvement: Lean supply chains emphasize a culture of constant evaluation and improvement. This involves regularly assessing processes and implementing changes to enhance efficiency and effectiveness.
- Just-In-Time (JIT) Inventory: The JIT approach ensures that materials and products are delivered exactly when needed, reducing storage costs and minimizing the risk of obsolescence.
- Customer-Centric Focus: Lean supply chains prioritize understanding and meeting customer needs. This includes delivering the right product, at the right time, and at the right cost.
Benefits of Lean Supply Chain Management
1. Cost Reduction
One of the most immediate benefits of implementing Lean principles is cost savings. By minimizing waste, reducing inventory, and optimizing transportation, companies can significantly lower operational costs. These savings can then be reinvested in other areas of the business or passed on to customers.
2. Improved Efficiency
Lean supply chains streamline operations, ensuring that resources are used as effectively as possible. This results in faster production cycles, reduced lead times, and more reliable delivery schedules.
3. Enhanced Agility
In today’s dynamic market environment, the ability to respond quickly to changes in demand is critical. Lean supply chains are more agile, enabling companies to adapt to market fluctuations without incurring significant additional costs.
4. Higher Quality
By focusing on value-added activities and continuous improvement, Lean supply chains often achieve higher levels of quality. This reduces the risk of defects, recalls, and customer dissatisfaction.
5. Sustainability
Lean practices contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing waste, optimizing resource usage, and minimizing carbon footprints. Companies that adopt Lean supply chain management not only benefit financially but also demonstrate a commitment to environmental responsibility.
Challenges in Implementing Lean Supply Chain Management
While the benefits of Lean supply chain management are significant, implementation is not without its challenges. Common obstacles include:
- Resistance to Change: Employees and stakeholders may resist adopting new processes or abandoning traditional practices.
- Initial Costs: Implementing Lean principles often requires upfront investment in training, technology, and process redesign.
- Complexity: Coordinating Lean practices across a global supply chain can be complex, especially when working with multiple suppliers and partners.
- Cultural Shift: Achieving a truly Lean supply chain requires a cultural transformation within the organization, which can take time and effort.
Best Practices for Lean Supply Chain Management
- Engage Stakeholders: Secure buy-in from employees, suppliers, and partners by communicating the benefits of Lean and providing the necessary training.
- Leverage Technology: Utilize tools such as inventory management software, predictive analytics, and automation to enhance efficiency and transparency.
- Focus on Metrics: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) to monitor progress and identify areas for improvement.
- Collaborate with Suppliers: Work closely with suppliers to align goals, share data, and optimize processes across the supply chain.
Lean supply chain management is more than just a strategy; it is a philosophy that drives continuous improvement and value creation. By eliminating waste, prioritizing customer needs, and fostering a culture of innovation, companies can build supply chains that are not only efficient but also resilient and sustainable. For organizations willing to embrace the principles of Lean, the rewards are significant: lower costs, higher quality, and a stronger competitive position in the market.